
updates2mqtt¶
Summary¶
Let Home Assistant tell you about new updates to Docker images for your containers.
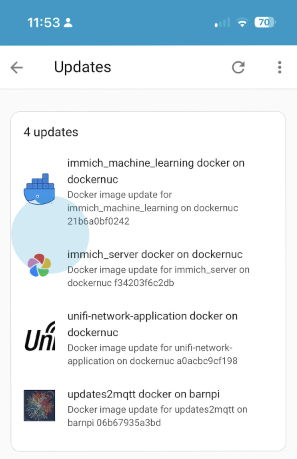
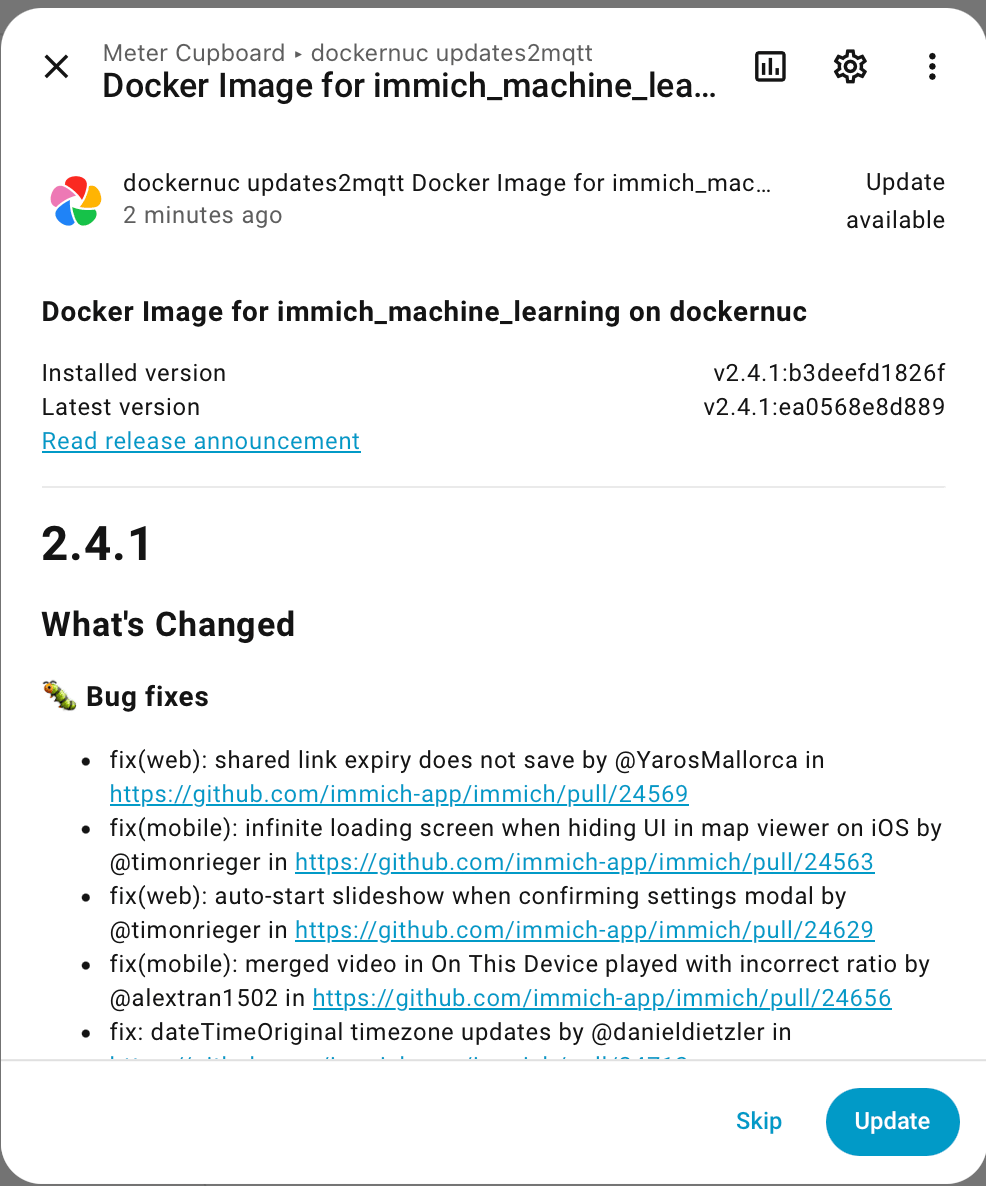
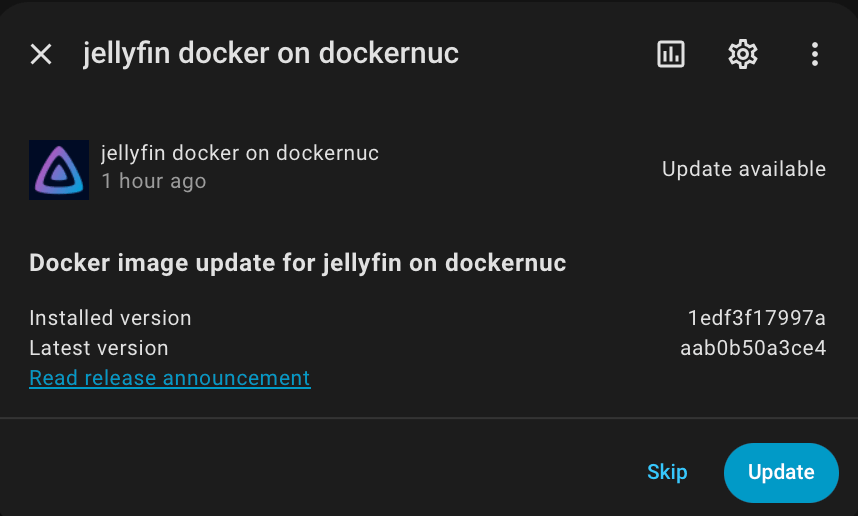
Read the release notes, and optionally click Update to trigger a Docker pull (or optionally build) and update.
Description¶
Updates2MQTT perioidically checks for new versions of components being available, and publishes new version info to MQTT. HomeAssistant auto discovery is supported, so all updates can be seen in the same place as Home Assistant’s own components and add-ins.
Currently only Docker containers are supported, either via an image registry check (using either v1 Docker APIs or the OCI v2 API), or a git repo for source (see Local Builds), with specific handling for Docker, Github Container Registry, Gitlab, Codeberg, Microsoft Container Registry, Quay and LinuxServer Registry, with adaptive behaviour to cope with most others. The design is modular, so other update sources can be added, at least for notification. The next anticipated is apt for Debian based systems.
Components can also be updated, either automatically or triggered via MQTT, for example by hitting the Install button in the HomeAssistant update dialog. Icons and release notes can be specified for a better HA experience. See Home Assistant Integration for details.
To get started, read the Installation and Configuration pages.
For a quick spin, try this:
docker run -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -e MQTT_USER=user1 -e MQTT_PASS=user1 -e MQTT_HOST=192.168.1.5 ghcr.io/rhizomatics/updates2mqtt:latest
or without Docker, using uv
export MQTT_HOST=192.168.1.1;export MQTT_USER=user1;export MQTT_PASS=user1;uv run --with updates2mqtt python -m updates2mqtt
It also comes with a basic command line tool that will perform the analysis for a single running container, or fetch manifests, JSON blobs and lists of tags from remote registries (known to work with GitHub, GitLab, Codeberg, Quay, LSCR and Microsoft MCR).
Release Support¶
Presently only Docker containers are supported, although others are planned, probably with priority for apt.
| Ecosystem | Support | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Docker | Scan. Fetch | Fetch is docker pull only. Restart support only for docker-compose image based containers. |
Heartbeat¶
A heartbeat JSON payload is optionally published periodically to a configurable MQTT topic, defaulting to healthcheck/{node_name}/updates2mqtt. It contains the current version of Updates2MQTT, the node name, a timestamp, and some basic stats.
Healthcheck¶
A healthcheck.sh script is included in the Docker image, and can be used as a Docker healthcheck, if the container environment variables are set for MQTT_HOST, MQTT_PORT, MQTT_USER and MQTT_PASS. It uses the mosquitto-clients Linux package which provides mosquitto_sub command to subscribe to topics.
Tip
Check healthcheck is working using docker inspect --format "{{json .State.Health }}" updates2mqtt | jq (can omit | jq if you don’t have jsonquery installed, but much easier to read with it)
Another approach is using a restarter service directly in Docker Compose to force a restart, in this case once a day:
restarter:
image: docker:cli
volumes: ["/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"]
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "while true; do sleep 86400; docker restart updates2mqtt; done"]
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- UPD2MQTT_UPDATE=AUTO
Target Containers¶
While updates2mqtt will discover and monitor all containers running under the Docker daemon, there are some options to make to those containers to tune how it works.
These happen by adding environment variables or docker labels to the containers, typically inside an .env file, or as environment options inside docker-compose.yaml.
Automated updates¶
If Docker containers should be immediately updated, without any confirmation or trigger, e.g. from the HomeAssistant update dialog, then set an environment variable UPD2MQTT_UPDATE in the target container to Auto ( it defaults to Passive). If you want it to update without publishing to MQTT and being visible to Home Assistant, then use Silent.
restarter:
image: docker:cli
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "while true; do sleep 86400; docker restart mailserver; done"]
environment:
- UPD2MQTT_UPDATE=AUTO
Automated updates can also apply to local builds, where a git_repo_path has been defined - if there are remote commits available to pull, then a git pull, docker compose build and docker compose up will be executed.
Related Projects¶
Other apps useful for self-hosting with the help of MQTT:
- psmqtt - Report system health and metrics via MQTT
Find more at awesome-mqtt
For a more powerful Docker focussed update manager, try What’s Up Docker
Development¶
This component relies on several open source packages:
- docker-py SDK for Python for access to Docker APIs
- Eclipse Paho MQTT client
- OmegaConf for configuration and validation
- structlog for structured logging and rich for better exception reporting
- hishel for caching metadata
- httpx for retrieving metadata
- The Astral uv and ruff tools for development and build
- pytest and supporting add-ins for automated testing
- usingversion to log current version info


